Sydney researcher Lidia Matesic has developed a technique to speed up the development of nuclear medicines allowing hospitals to not only make nuclear medicine in-house, but also tailor-made to the patient.
In remote hospitals, this would also allow a larger variety of these pharmaceuticals to be used.
“We have some nuclear medicines that work extremely well for particular diseases, like radiotherapy for cancer,” says Lidia. “But we need more-specific nuclear medicines for other diseases, such as Alzheimer’s.”
These new drugs can take years to develop – but faster reactions and processes would allow researchers to develop new nuclear medicines faster.
Lidia is working to speed up these processes using ‘microfluidic technology’ which makes chemical reactions faster by using less liquid. Down from millilitres to millionths of a litre.
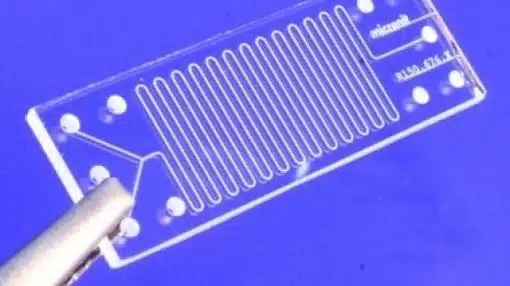
These microfluidic devices contain tiny, intricate structures of tubes that could fit easily within a matchbox. The components of the machinery are miniscule – only hundredths of a millimetre in dimension.
Her lab at the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) in Sydney is the only one of its kind in the Southern Hemisphere.
“Using this technology, it’s possible we could move into pre-clinical trials in weeks – and towards human trials of a new medicine much faster than with previous technology.”
The concept, known as dose-on-demand, is particularly important with radiopharmaceuticals because the active radioactive components of the medicine decay quickly (in as little as minutes or a few hours).
The research is published in Nuclear Medicine and Biology.
Contact: Lidia Matesic, Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation, (02) 9717 7606, lidia.matesic@ansto.gov.au

Lidia Matesic’s microfludic device could lead to faster drug discovery.




 Fresh Science is on hold for 2022. We will be back in 2023.
Fresh Science is on hold for 2022. We will be back in 2023.